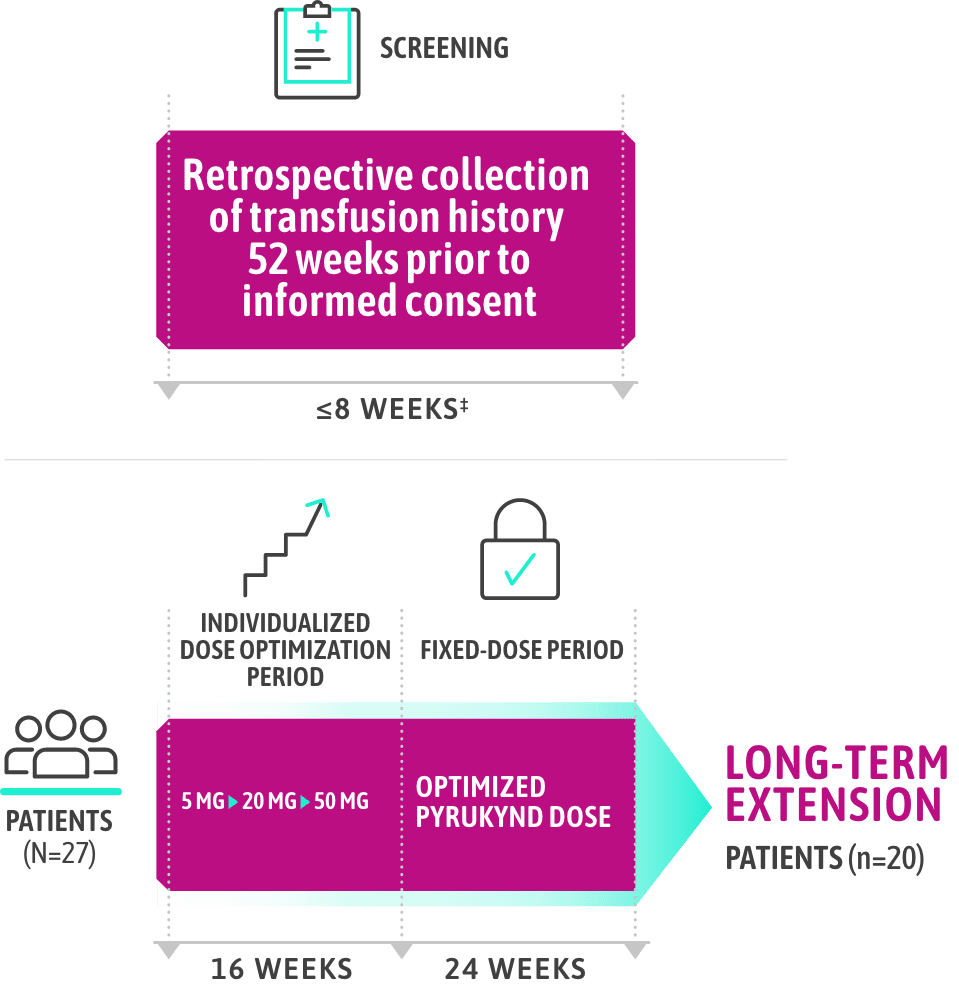
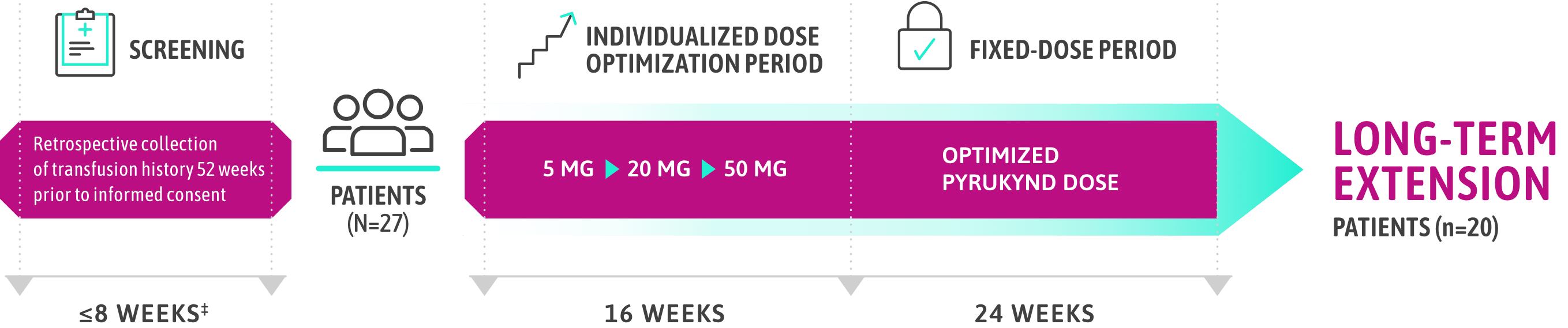
ACTIVATE-T: PATIENTS WHO WERE REGULARLY TRANSFUSED
PYRUKYND® (mitapivat) delivered clinically meaningful transfusion reductions1
Indication
PYRUKYND is a pyruvate kinase activator indicated for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency.
Important Safety Information
Acute Hemolysis: Acute hemolysis with subsequent anemia has been observed
following abrupt interruption or discontinuation of PYRUKYND in a dose-ranging study. Avoid abruptly discontinuing PYRUKYND. Gradually taper the dose of PYRUKYND to discontinue treatment if possible. When discontinuing treatment, monitor patients for signs of acute hemolysis and anemia including jaundice, scleral icterus, dark urine, dizziness, confusion, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
Indication
PYRUKYND is a pyruvate kinase activator indicated for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency.
Important Safety Information
Acute Hemolysis: Acute hemolysis with subsequent anemia has been observed following abrupt interruption or discontinuation of PYRUKYND in a dose-ranging study. Avoid abruptly discontinuing PYRUKYND. Gradually taper the dose of PYRUKYND to discontinue treatment if possible. When discontinuing treatment, monitor patients for signs of acute hemolysis and anemia including jaundice, scleral icterus, dark urine, dizziness, confusion, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
Hepatocellular Injury in Another Condition: In patients with another condition treated with PYRUKYND at a higher dose than that recommended for patients with PK deficiency, liver injury has been observed. These events were characterized by a time to onset within the first 6 months of treatment with peak elevations of alanine aminotransferase of >5x upper limit of normal (ULN) with or without jaundice. All patients discontinued treatment with PYRUKYND, and these events improved upon treatment discontinuation.
Obtain liver tests prior to the initiation of PYRUKYND and monthly thereafter for the first 6 months and as clinically indicated. Interrupt PYRUKYND if clinically significant increases in liver tests are observed or alanine aminotransferase is >5x ULN. Discontinue PYRUKYND if hepatic injury due to PYRUKYND is suspected.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions including laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) in patients with PK deficiency were estrone decreased (males), increased urate, back pain, estradiol decreased (males), and arthralgia.
Drug Interactions:
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers: Avoid concomitant use.
- Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Do not titrate PYRUKYND beyond 20 mg twice daily.
- Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Consider alternatives that are not moderate inducers. If there are no alternatives, adjust PYRUKYND dosage.
- Sensitive CYP3A, CYP2B6, CYP2C Substrates Including Hormonal Contraceptives: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index.
- UGT1A1 Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index.
- P-gp Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with substrates that have narrow therapeutic index.
Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use of PYRUKYND in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment.
Please see full Prescribing Information for PYRUKYND.